Following the release of ISO 27002:2022 in February, the International Organisation for Standardization published the new ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Information Security, Cybersecurity, and Privacy Protection – Information Security Management Systems – Requirements in October.
With the rapid adoption of digital transformation and the ever-evolving cyber threat landscape, the standard has been revised with the addition of new controls, like Threat Intelligence, Cloud Services and Secure Coding. This aims to address global cyber security challenges and to guide organisations in improving digital trust.
There are two parts to an ISO 27001 standard, the core requirements – Clauses 4 to 10, supported by a set of security controls, known as Annex A. The Annex A provides organisation guidance and ensures that no security controls are missed during implementation.
Overall, the intent of the standard remains the same, with the core fundamental aspects of risk management being unchanged. Taking on a risk-based approach, the standard protects the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets.
The core requirements generally remain the same, with slight additions and enhancements to phrasings.
- Clause 4.2 (Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties),
now includes identifying the requirements of interested parties that will be addressed through ISMS. - Clauses 4.4 (Information security management system),
a new phrase was added, requiring the planning for processes and their interactions as part of the ISMS. - Clause 5.3 (Organizational roles, responsibilities and authorities),
a new phrase was added to explain that communication of roles is done internally within the organization - Clause 6.2 (Information security objectives and planning to achieve them),
now includes a monitoring capability of information security objectives. - (NEW) Clause 6.3 (Planning of changes),
includes having a plan for any changes to the ISMS. - Clause 7.4 (Communication),
item (e) was deleted, which was the requirement on setting up processes for communication. - Clause 8.1 (Operational planning and control)
now includes establishing criteria for security processes and implementing process. The requirement to implement plans for achieving objectives has been deleted. - Clause 9.3 (Management Review)
now includes reviewing the changes in needs and expectations of interested parties, and relevant to the ISMS. - Clause 10 (Improvement),
the text of the clauses remained unchanged. The subclauses have changed places, with first being, Continual improvement (10.1), and the second is Nonconformity and corrective action (10.2).
The changes in Annex A are reflective of the changes made in the new ISO 27002:2022, published in February 2022, which is a supplementary standard for implementing ISO 27001.
Revised from “reference control objectives and controls” to “information security controls reference”, there are significant uplifts and updates to Annex A.
The key changes include the following:
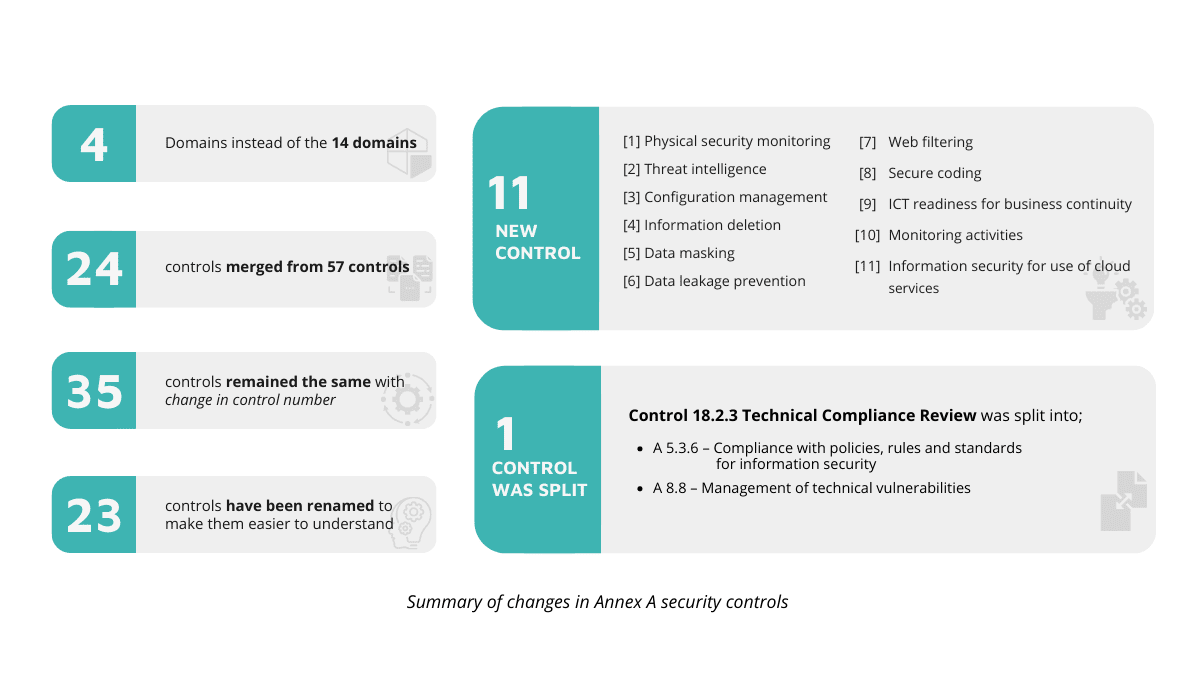
- The controls are regrouped into four domains – Organisational, People, Physical and Technology instead of the previous 14.
- The total number of controls has decreased from 114 to 93.
No controls have been excluded, with some merged for rationalisation and effectiveness. Hence the reduction in the number of controls.- 57 controls merged into 24 controls.
- 35 controls remained the same with a change in control number.
- 23 controls have been renamed.
- Only one control was split, Control 18.2.3 Technical Compliance Review:
- 5.3.6 – Compliance with policies, rules and standards for information security.
- 8.8 – Management of technical vulnerabilities
- The concept of attributes has been introduced.
- Control Type
- Information Security Properties
- Cybersecurity Concepts
- Operational Capabilities
- Security Domains
- 11 new security controls has been added.
- A.5.7 Threat intelligence
- A.5.23 Information security for use of cloud services
- A.5.30 ICT readiness for business continuity
- A.7.4 Physical security monitoring
- A.8.9 Configuration management
- A.8.10 Information deletion
- A.8.11 Data masking
- A.8.12 Data leakage prevention
- A.8.16 Monitoring activities
- A.8.23 Web filtering
- A.8.28 Secure coding
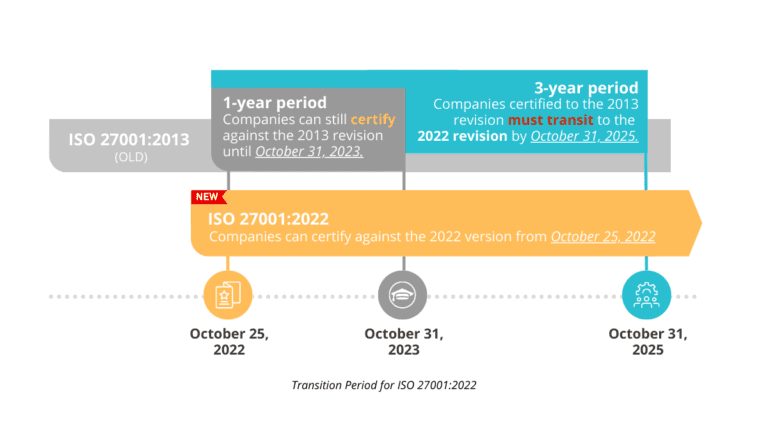
You can still certify your ISMS to the 2013 version, by latest 31 October 2023. Thereafter, your organisation would still have to transit to 2022 version – ISO 27001:2022, prior to the end of the transition period (31 October 2025).
However, if you now plan to certify to the latest 2022 version, you can do so without any loss of effort spent to date, as the updates from ISO 27001:2013 to ISO 27001:2022 requires enhancements and remapping to the new Annex A controls.
There are no impacts on the existing certifications.
From the release, October 2022, there is a 3-year time window (by 31 October 2025) for organisations to transit to the new standard. When possible, this can be done as part of the 3-year recertification audit, arranged during the yearly surveillance audit, or a standalone assessment.
- Conduct a gap assessment against the new standard, to align with the new ISO 27001:2022 requirements
- Update your Statement of Applicability (SoA) to align with the updated ISO 27001:2022 Annex A
- Review your risk and actions register to ensure alignment with the revised standard and controls.
- Review and update your documentation, including policies and procedures to meet both the update and new controls applicable to your ISMS.
Schedule a consultation with us and we can help with your transition to the new ISO 27001:2022 Certification or if you would like to find out more about the new ISO 27001:2022 standard
Privasec is an ISO 9001 and ISO 27001 certified independent cyber security consulting firm with a Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) team of highly experienced and certified professionals, each with an average of 10 years of cyber security consulting experience.
With great expertise and a commendable proven track record of implementing an Information Security Management System (ISMS) that is certifiable to ISO 27001, we are glad to assist and support organisations on their ISO 27001 Certification journey.
Secure your business with us
Simply drop us an email at [email protected] or call us at +65 6610 9597 (SG) / 1800 996 001 (AU) for more details